No products in the cart.
India Quick Service Restaurants Market
- Brand: DigiRoads
The India Quick Service Restaurants Market Report provides a comprehensive analysis of market trends, key players, growth factors, and consumer preferences. With insights into market size, segmentation, and future projections, this 120-page report is a valuable resource for industry stakeholders.
Category: Food and Beverage
Brand: DigiRoads
India Quick Service Restaurants Market Report | Market Size, Industry Analysis, Growth Opportunities, & Forecast (2025-2030)
India Quick Service Restaurants Market Overview
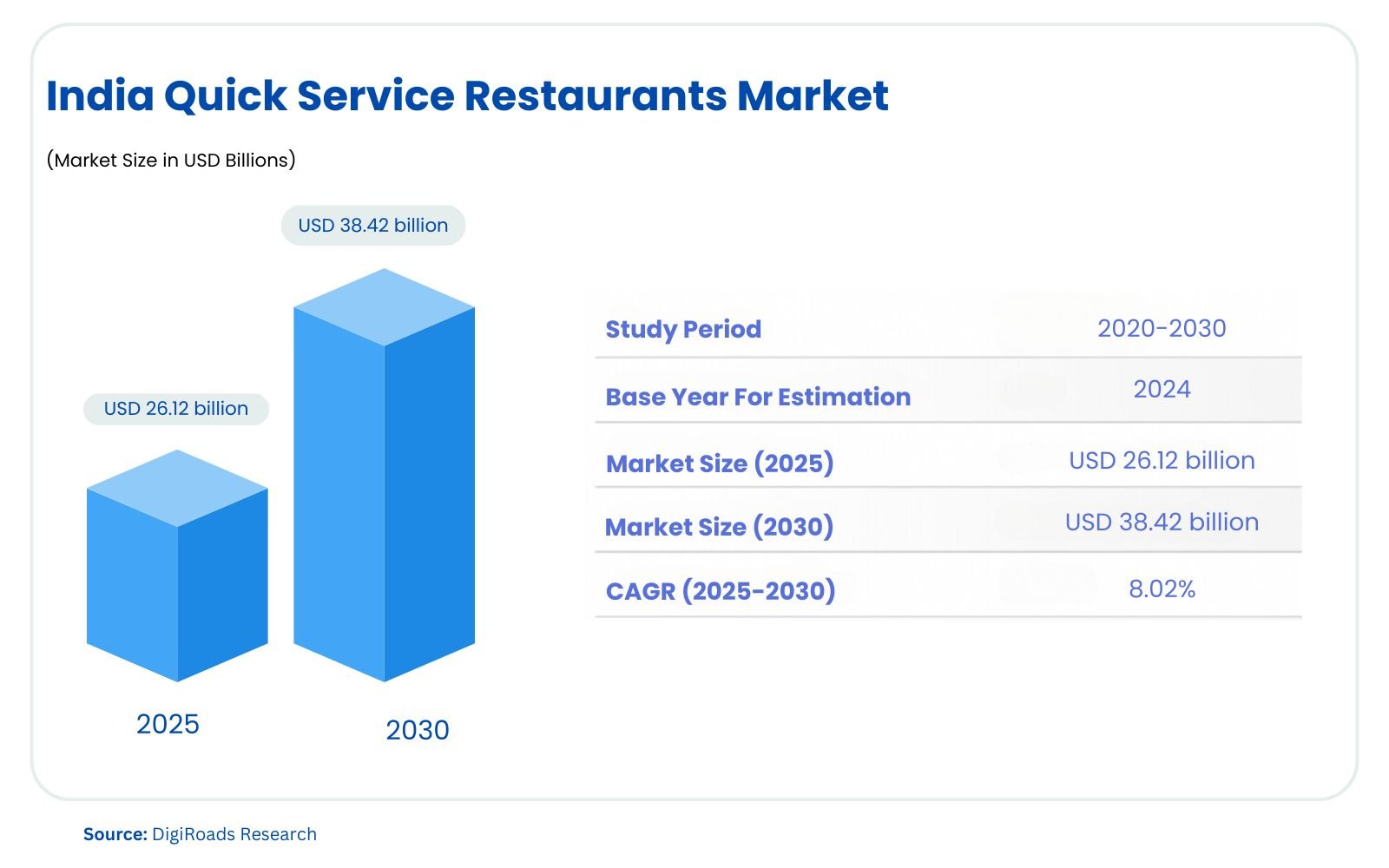
The India Quick Service Restaurants Market is on an upward trajectory, with an estimated market size of USD 26.12 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach USD 38.42 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 8.02% during the forecast period 2025-2030. The India Quick Service Restaurant (QSR) Market is rapidly expanding, driven by a growing demand for fast, convenient, and affordable dining options. Key factors fueling this growth include increasing consumer preference for fast delivery options, hygienic food, and a variety of customizable meal choices. Additionally, the rise of millennials and their penchant for smart-eating habits have significantly contributed to the surge in sales.
Popular items like burgers, pizzas, and chicken-based dishes dominate the market, with pizza projected to grow at a high CAGR during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market is also witnessing a shift towards independent QSR outlets, which offer lower-priced products compared to chain stores, making them an attractive option for consumers.
Leading global brands like McDonald’s, Domino’s, KFC, and Yum! Brands continue to expand their presence, with increasing numbers of outlets across both metro and non-metro cities. This report provides in-depth analysis and insights into the India QSR market trends, key players, and growth projections.
Market Report Coverage:
The “India Quick Service Restaurants Market Report—Future (2025-2030)” by Digiroads Research & Consulting covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments in the market.
| Popular Cuisine Types | Burgers, Pizza, Chicken-based dishes (wings, nuggets, etc.), Bakery products |
| Popular QSR Dishes | French fries, Pizzas, Sandwiches, Burgers, Wraps/Rolls, Garlic bread |
| By Region | North Region, West Region, South Region, East Region |
Study Assumptions and Definitions
This study of the India Quick Service Restaurants market assumes the continued growth of consumer demand for convenient, fast, and hygienic food options during the forecast period from 2025 to 2030. It assumes that technological advancements, such as faster delivery systems and online ordering platforms, will continue to drive the growth of QSRs. Additionally, an increase in consumer preference for healthier and customizable food choices is anticipated, which will influence the types of offerings in the market. The study further assumes that global brands like McDonald’s, Domino’s, and KFC will maintain their strong presence and expand further through both company-operated and franchised outlets, especially in metro and non-metro cities.
The term “Quick Service Restaurant (QSR)” refers to restaurants that provide fast food services with minimal table service, where customers typically order at the counter or via delivery platforms. “CAGR” (Compound Annual Growth Rate) refers to the rate of growth over a specific period, factoring in consistent expansion. “Metro cities” refer to major urban areas like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru, while “Non-metro cities” represent smaller towns and cities with emerging consumer bases. “Outlet types” distinguish between chain outlets (operated by large brands) and independent outlets, offering differentiated pricing and service models.
Market Scope
The scope of this study on the India Quick Service Restaurants market covers the period from 2025 to 2030, providing a detailed analysis of market size, growth trends, and key drivers. The market scope includes insights into popular QSR dishes, such as burgers, pizzas, chicken-based products, and bakery items, along with consumer preferences for fast and hygienic food. It examines the market’s expansion across both metro and non-metro regions, highlighting significant growth in states like Delhi, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh.
The scope also includes an analysis of outlet types, focusing on the growth of independent outlets, which are becoming increasingly popular due to lower pricing compared to chain stores. The study further explores the competitive landscape, identifying key players such as McDonald’s, Domino’s, KFC, and local brands. It evaluates market trends, technological advancements, and the influence of millennials on the demand for fast food and delivery services in India.
MARKET OUTLOOK
Executive Summary
The India Quick Service Restaurants market is poised for significant growth from 2025 to 2030, driven by an increasing demand for fast, convenient, and hygienic dining options. The market is expected to grow from USD 26.12 billion in 2025 to USD 38.42 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.02%. This growth is largely attributed to the rising preference for fast food among India’s youth, particularly millennials, who are seeking quick, customizable, and affordable meals.
Key drivers of the market include the expanding reach of global QSR brands such as McDonald’s, Domino’s, KFC, and Yum! Brands, along with a surge in online ordering and delivery platforms. The growing trend of fast, hygienic, and customizable meals further supports market growth. Additionally, the increasing popularity of chicken-based dishes, pizzas, and bakery products has bolstered the demand for QSR services. Pizza, in particular, is expected to be the fastest-growing cuisine, projected to see a rapid CAGR during the forecast period.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards independent outlets, which offer products at 30-40% lower prices than chained stores, making them attractive to a broad customer base.
Geographically, the market is expanding across both metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Chennai, and non-metro cities such as Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Maharashtra. Consumer spending on fast food has risen significantly, with the average order value increasing by around 25% from 2025 to 2030. The increased number of QSR outlets and the rise in per capita meat consumption further contribute to this growth, which is expected to continue in the coming years.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The India Quick Service Restaurants Market is moderately fragmented, with regional and multinational players competing fiercely for market share.
Key Market Players
- Coffee Day Enterprises Limited
- Doctor’s Associate, Inc. (Subway)
- Jubilant FoodWorks Limited (Domino’s)
- McDonald’s Corporation
- Yum! Brands, Inc. (KFC, Pizza Hut)
- Graviss Foods Private Limited
- Restaurant Brands Asia Limited (Burger King)
- Tata Starbucks Private Limited
- Wow! Momo Foods Private Limited
- Hardcastle Restaurants Pvt. Ltd. (McDonald’s India – West & South)
Market Share Analysis
The India Quick Service Restaurants market is highly competitive, with global and regional brands vying for market share. As of the latest analysis, the market remains fragmented, with the top five players occupying only around 5% of the overall market share. Leading global brands such as McDonald’s, Domino’s (Jubilant FoodWorks), KFC (Yum! Brands), and Subway (Doctor’s Associate, Inc.) dominate the sector, largely due to their extensive franchised networks and brand recognition.
Domino’s, for example, is a significant player in the pizza segment, with a strong presence in metro and non-metro cities. McDonald’s has a well-established footprint, particularly in the southern and western regions, while KFC continues to capture substantial share in the chicken-based QSR segment. Starbucks and Tata Starbucks focus on the coffee and beverages market, contributing to the diversity of offerings in the QSR space.
Regional and independent outlets, such as Wow! Momo Foods, Haldiram’s, and Bikanervala, are growing at a faster rate due to lower pricing and increasing consumer interest in local, affordable options. Independent outlets are projected to experience the highest growth, compared to established chain brands.
In conclusion, while global players retain substantial market dominance, local chains and independent outlets are gaining traction, driving increased competition and innovation in the India QSR market.
MARKET DYNAMICS
Market Drivers and Key Innovations
- Rising Consumer Demand for Convenience: The growing preference for fast, convenient, and hygienic food options is a major driver of the India Quick Service Restaurant (QSR) market. Busy lifestyles and the need for quick meal solutions, especially among millennials and working professionals, have led to increased demand for QSR outlets, particularly those offering fast delivery and takeout options.
- Expansion of Global QSR Brands: The increasing presence of global fast-food giants like McDonald’s, Domino’s, and KFC has significantly contributed to market growth. Their extensive franchised networks and aggressive expansion into both metro and non-metro cities across India have made quick-service food more accessible to a larger audience.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of online ordering platforms and food delivery apps has fueled the growth of QSRs. Technologies like app-based ordering, delivery within 30 minutes, and innovative packaging (e.g., oven bags for pizza delivery) have enhanced customer experience and convenience, further driving demand.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: There is a growing trend toward healthier and customizable food choices. Consumers are seeking meals that cater to specific dietary needs, leading to a shift in QSR offerings, including vegan, low-calorie, and gluten-free options.
Key Innovations:
- Faster Delivery Technology: Innovations in delivery technology, including optimized routing algorithms and enhanced logistics, ensure quicker delivery times, often within 30 minutes, which appeals to consumers seeking convenience.
- Smart Packaging: QSR chains have adopted innovative packaging solutions, such as oven bags used by pizza chains, to ensure food stays hot and fresh during delivery.
- Customizable Menus: Offering customizable food options has become a popular innovation, allowing consumers to create meals tailored to their preferences and dietary restrictions, fostering greater customer loyalty.
Market Challenges
- Intense Competition: The market is highly fragmented with numerous global and regional players competing for market share. Established global brands and emerging local chains create a highly competitive environment, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
- Rising Operating Costs: The cost of ingredients, rent, and labor has been rising in India, affecting profitability for QSR operators. Increased inflation and supply chain disruptions can further put pressure on pricing and margins.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: While there is a growing demand for fast food, consumers are also becoming more health-conscious and seeking healthier food options. This shift in preference forces QSR brands to constantly innovate and adapt their menus to meet evolving consumer demands.
- Regulatory Challenges: The food service industry in India is heavily regulated, with varying state-level regulations on food safety, hygiene standards, and licensing requirements. Compliance with these regulations can be a challenge for QSR operators, particularly in non-metro regions.
- Labor Shortages: The QSR sector faces challenges in maintaining a consistent and skilled workforce. Labor shortages, especially in non-metro cities, can impact the quality of service and operational efficiency.
- Delivery Infrastructure and Costs: While food delivery has grown rapidly, managing delivery logistics, maintaining food quality, and controlling delivery costs remain significant challenges for QSRs, particularly for smaller players.
- Price Sensitivity: Indian consumers are highly price-sensitive, and the QSR sector must balance affordability with quality. Price increases due to inflation or rising operational costs can lead to a reduction in customer footfall.
Market Opportunities
- Expansion into Tier 2 and Tier 3 Cities: With increasing urbanization and rising disposable incomes, there is significant untapped potential in smaller cities and towns. QSRs can expand into these regions, where demand for fast and affordable meals is growing.
- Growth in Online Ordering and Delivery: The continued rise in online food delivery services offers an opportunity for QSRs to reach a broader audience. Partnering with popular food delivery platforms or investing in proprietary delivery systems can help capture a larger market share.
- Introduction of Health-Conscious Menus: As consumer preferences shift towards healthier eating, QSRs can capitalize on this trend by offering nutritious, low-calorie, and plant-based menu options. Vegan, gluten-free, and organic choices can attract health-conscious consumers.
- Increasing Popularity of Breakfast Menus: The demand for breakfast items such as sandwiches, wraps, and beverages is growing. QSRs can tap into this market by introducing specialized breakfast menus, catering to the increasing number of people opting for quick breakfast options.
- Customization and Personalization: Offering customizable meals where customers can choose ingredients according to their preferences and dietary needs can help QSR brands stand out. Personalization, including customization in portion sizes, toppings, and flavors, appeals to the growing trend of individualized dining experiences.
- Technological Innovations: Embracing new technologies such as AI-driven delivery systems, self-order kiosks, and contactless payment solutions can improve efficiency, reduce wait times, and enhance the customer experience.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Increasing consumer demand for sustainability presents an opportunity for QSRs to adopt eco-friendly practices. Using biodegradable packaging, sourcing locally produced ingredients, and reducing food waste can enhance brand loyalty among environmentally conscious consumers.
RECENT STRATEGIES & DEVELOPMENTS IN THE MARKET
Expansion of Outlet Networks:
- Jubilant FoodWorks plans to open 250 new Domino’s stores in India within the next 12-18 months, with a capital investment of INR 900 crore (approximately USD 110 million).
- Subway was acquired by Roark Capital for USD 8.95 billion in August 2023, signaling an expansion strategy aimed at growth in India and other emerging markets.
- KFC and Subway are opening new stores in cities like Delhi and Punjab in 2023, and both brands plan to expand further by 2024.
Introduction of New Menu Items:
- Popeyes India introduced a new Shrimp Roll to its seafood menu in January 2023 to cater to the growing demand for seafood and diversify its offerings.
- McDonald’s and KFC have expanded their dessert menus to include products like Choco Lava Cakes, capitalizing on the growing popularity of indulgent desserts in the QSR sector.
Shift to Digital Ordering and Delivery:
- The rise of online ordering platforms and food delivery apps continues to shape QSR operations. Many brands are enhancing their mobile apps to offer smoother, faster services.
- Domino’s India has been at the forefront of leveraging delivery technology with delivery guarantees (30-minute delivery) and app-based ordering systems to improve customer experience.
Focus on Sustainability:
- Domino’s and McDonald’s are introducing more eco-friendly practices, such as the use of biodegradable packaging. These sustainability efforts are aligned with growing consumer interest in reducing environmental impact.
- Starbucks (Tata Starbucks Pvt. Ltd.) is promoting sustainability with initiatives like introducing paper straws and reducing plastic use in its operations.
Price Adjustments to Adapt to Inflation:
- To combat inflation and rising costs, many QSR brands have slightly adjusted menu prices, with an average increase of 5-7% from 2025 to 2030. This price adjustment is necessary to maintain profitability while catering to price-sensitive Indian consumers.
- Independent outlets have capitalized on the price-conscious consumer base by offering products 30-40% cheaper than chain outlets.
Increased Investment in Regional Markets:
- QSR chains are increasingly focusing on non-metro cities for expansion. For instance, Domino’s and KFC are tapping into regional markets in Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Punjab. This strategy is aimed at tapping into the growing demand from smaller cities where disposable incomes are rising.
Health-Conscious Menus and Customization:
- McDonald’s and Subway have introduced healthier menu options, such as salads, low-calorie meals, and plant-based choices, in response to the growing health-conscious consumer base.
- Many QSRs are offering customization options, allowing customers to personalize their meals, catering to dietary needs like gluten-free or vegan preferences.
KEY BENEFITS FOR STAKEHOLDERS
For Investors:
- High Growth Potential: The rapid expansion of global and regional QSR brands in India offers significant returns on investment. The market is projected to grow at a high CAGR from 2025-2030, ensuring lucrative opportunities.
- Diversification of Portfolio: Investing in QSR brands provides a diversified exposure to the foodservice industry, balancing risks in other sectors.
- Stable Revenue Streams: With a growing demand for fast and convenient food options, QSRs offer stable, recurring revenue from both in-store dining and online delivery.
For QSR Operators:
- Scalability: QSR models, especially franchised outlets, offer scalability with relatively low capital investment. Expanding in tier 2 and tier 3 cities presents untapped potential for growth.
- Brand Recognition: Leveraging the popularity of established global brands (e.g., McDonald’s, Domino’s, KFC) allows operators to benefit from strong brand equity and customer loyalty.
- Innovation Opportunities: Operators have opportunities to innovate in menu offerings (e.g., healthy, customizable meals) and delivery systems, meeting evolving consumer demands.
For Consumers:
- Convenience and Affordability: Consumers enjoy faster service and greater convenience, with QSRs offering quick meal solutions at affordable prices.
- Variety and Customization: A wide range of food choices, including healthier options, customization, and local flavors, caters to diverse tastes and dietary preferences.
- Better Quality and Hygiene: Increased focus on hygiene and the introduction of quality standards in the industry provide consumers with greater confidence in their food choices.
For Suppliers:
- Increased Demand for Ingredients: The rapid expansion of QSRs boosts demand for food ingredients, packaging, and delivery services, offering suppliers significant growth opportunities.
- Long-Term Partnerships: Strong demand for bulk ingredients and local sourcing options creates opportunities for suppliers to establish long-term partnerships with QSR brands.
For Franchisees:
- Lower Capital Requirement: Franchisees can benefit from lower initial capital investment and risk due to the established business model and brand recognition of global QSR chains.
- Ongoing Support: Franchisees receive marketing, operational, and training support, which increases their chances of success and profitability.
At DigiRoads Research, we emphasize reliability by employing robust market estimation and data validation methodologies. Our insights are further enhanced by our proprietary data forecasting model, which projects market growth trends up to 2030. This forward-thinking approach ensures our analysis not only captures the current market landscape but also anticipates future developments, equipping stakeholders with actionable foresight.
We go a step further by offering an exhaustive set of regional and country-level data points, supplemented by over 60 detailed charts at no additional cost. This commitment to transparency and accessibility allows stakeholders to gain a deep understanding of the industry’s structural and operational dynamics. By providing exclusive and hard-to-access data, DigiRoads Research empowers businesses to make informed strategic decisions with confidence.
In essence, our methodology and data delivery foster a collaborative and data-driven decision-making environment, enabling businesses to navigate industry challenges and capitalize on opportunities effectively.
Contact Us For More Inquiry.
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
- Market Overview
- Years Considered for Study
- Market Segmentation
- Study Assumptions and Definitions
- Market Scope
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
MARKET OUTLOOK
- Executive Summary
- Market Snapshot
- Market Segments
- Popular Cuisine Types
- Burgers
- Pizza
- Chicken-based dishes (wings, nuggets, etc.)
- Bakery products
- Popular QSR Dishes
- French fries
- Pizzas
- Sandwiches
- Burgers
- Wraps/Rolls
- Garlic bread
- By Region:
- North Region
- West Region
- South Region
- East Region
- Popular Cuisine Types
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- Recent Strategies (Key Strategic Moves)
- Market Share Analysis
- Company Profiles
- Coffee Day Enterprises Limited
- Doctor’s Associate, Inc. (Subway)
- Jubilant FoodWorks Limited (Domino’s)
- McDonald’s Corporation
- Yum! Brands, Inc. (KFC, Pizza Hut)
- Graviss Foods Private Limited
- Restaurant Brands Asia Limited (Burger King)
- Tata Starbucks Private Limited
- Wow! Momo Foods Private Limited
- Hardcastle Restaurants Pvt. Ltd. (McDonald’s India – West & South)
- Popeyes India (Restaurant Brands International)
- Sagar Ratna (Indian QSR Chain)
- Bikanervala Foods Pvt. Ltd.
- Haldiram’s (Haldiram Snacks)
- Krispy Kreme Doughnuts Inc. (Krispy Kreme India)
MARKET DYNAMICS
- Market Drivers
- Market Challenges
- Market Opportunities
- Porter’s Five Forces’ Analysis
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Threat of New Entrant
- Threat of Substitutes
- Competitive Rivalry
GLOSSARY OF PROMINENT SECONDARY SOURCES
DISCLAIMER
ABOUT US